
Biometrics Recognition
Introduction
With the rapid development of modern digital society, how to perform security personal authentication plays a foundation role for various practical applications. Biometrics, which automatically recognizes individuals by using one’s distinct physiological or behavioral traits, has served as one the most effective technologies for personal authentication and also played an increasingly important role in the national economy. In recent years, deep learning technologies have achieved impressive performance in various pattern recognition and computer vision tasks, which has also be successfully applied in biometric recognition, profoundly changing the directions of biometric recognition technology. For this reason, it is highly necessary to convene a biometric recognition technology forum to discuss the latest development of biometric recognition technology. At this forum, four outstanding young scholars will provide interesting and valuable technical reports on several important biometric recognition fields, including the trustworthy face recognition, face anti-spoofing, animal biometric recognition, and vein recognition. At this forum, attendees can better study the latest progress in the above directions of biometrics. Moreover, through a panel discussion, the attendees can further understand and discussion the future potential development directions of biometric recognition technology. Therefore, this forum is of great significance for researchers in the related fields of biometric recognition.
Schedule
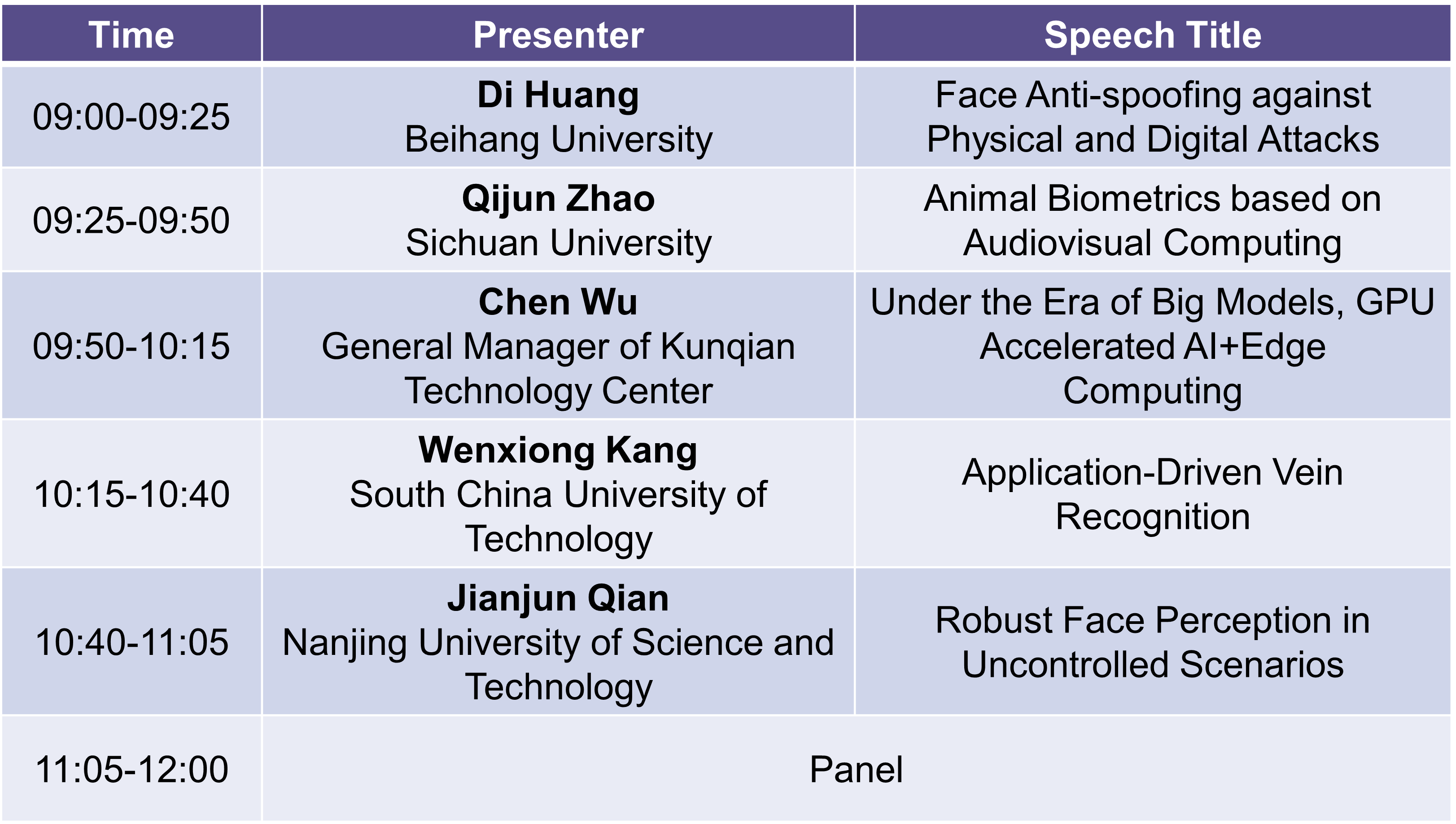
Sept. 22th 09:00-12:00
Organizers

Wei Jia
Hefei University of Technology
Biography:Wei Jia received the B.Sc. degree in informatics from Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China, in 1998, the M. Sc. Degree in computer science from the Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, in 2004, and the Ph.D. degree in pattern recognition and intelligence system from the University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, in 2008. He is currently a professor and doctoral supervisor of School of Computer and Information Science, Hefei University of Technology, and also the Deputy Director and Secretary General of the Youth Work Committee of the Chinese Society of Graphic Arts. He had served as the procedural and organizational chairpersons of renowned international and domestic conferences for over 20 times. His research interests include computer vision, biometrics, pattern recognition, image processing, and machine learning. He has published more than 100 scientific papers, including more than 40 papers in CCF Class A and top journals such as IEEE Transactions. The papers have been cited more than 5000 times with an H-factor of 35. He now serves as an editorial board member of the Chinese Journal of Image and Graphics.

Lunke Fei
Guangdong University of Technology
Biography:Lunke Fei received the Ph. D. degree in computer science and technology from the Harbin Institute of Technology, China, in 2016. He is currently an Associate Professor with the School of Computer Science and Technology, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, and the CCF/CSIG/IEEE Senior member. His research interests include pattern recognition, biometrics and image processing. He has published more than 60 papers at prestigious international journals and conferences, including more than 30 papers in CCF-A conference or IEEE Transactions. His paper has more than 4500 Google Scholar citations and the H-index is 33. He is now an editorial board member of International Journal of Biometrics (IJBM), an associate editor of International Journal of Image and Graphics (IJIG) and a young editorial board member of IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica.
Presenters

Di Huang
Beihang University
Biography:Dr. Di Huang is currently a Professor with the School of Computer Science and Engineering at Beihang University. His research interests include biometrics, 2D/3D face analysis, pattern recognition and image/video processing. He has worked as the PI or key participant in many international and national grants, e.g., NSFC and ANR. He has authored more than 80 papers at prestigious international journals and conferences with around 8,500 citations received. He has won academic paper awards for 5 times, including ICB and AMFG, as well as champions of challenges at top-tier conferences, such as MM and ICRA. Related techniques are successfully applied in the industry.
Speech Title:Face Anti-spoofing against Physical and Digital Attacks
Abstract:In recent years, there has been a rapid emergence of facial perception applications, which are playing a crucial role in key domains, such as access control and financial payment, and enhancing the convenience of people’s lives. However, the large advances in 3D printing and deep learning technologies also lead to more vivid face forgeries, significantly threating the security of biometric authentication systems. This talk focuses on face anti-spoofing, presenting the latest progress of physical and digital attack detection by the research team. In particular, it shows the paradigm of detecting unknown spoofing types, the method of spatial and frequency feature learning, and the strategy of texture-geometry information fusion. In addition, thoughtful considerations on potential perspectives within this field are discussed.

Qijun Zhao
Sichuan University
Biography:Zhao Qijun, Ph.D., Professor, Vice Dean of College of Computer Science, Sichuan University. He obtained a bachelor’s and master’s degree in the Department of Computer Science and Technology of Shanghai Jiaotong University from 1999 to 2006, a doctor’s degree in the Department of Computing of Hong Kong Polytechnic University from 2006 to 2010. He used to serve as a postdoctoral researcher in Michigan State University, and a visiting professor in Tibet University. His research interest lies in the field of biometric recognition, and focuses on animal biometrics in recent years. He has been awarded the second prize of the Shanghai Natural Science Award, the third prize of the Sichuan Provincial Science and Technology Progress Award, an outstanding reviewer in CVPR2020, and an outstanding editorial board member of the Chinese Journal of Image Graphics.
Speech Title:Animal Biometrics based on Audiovisual Computing
Abstract:Identifying animal species and attributes, distinguishing individual animals, and understanding their behavior are of crucial value for wildlife monitoring and protection. In recent years, due to emerging deep learning technologies, computer vision and auditory computing have developed rapidly, providing potential more efficient solutions for identifying animals. In this talk, we will introduce the application of audio-visual computing technology in animal biometric recognition and report our recent research outcomes, including animal individual recognition or re recognition based on appearance features, as well as animal species recognition, attribute classification, and emotional analysis based on vocalization.

Chen Wu
Kunqian Technology Center
Biography:ZChen Wu, General Manager of Kunqian Technology Center, is a senior hardware engineer who has been working in the field of server computing for over 20 years. He has rich experience in server architecture and information construction, and has many years of work experience in security, computer, internet, artificial intelligence, and other fields. Currently serving as a member of the Professional Committee of the Jiangsu Artificial Intelligence Society.
Speech Title:Under the Era of Big Models, GPU Accelerated AI+Edge Computing
Abstract:With the release of GPT-4, the big language model has officially entered the era of multimodality, and the number of parameters has further expanded. SAM Altman, the founder of openAI, stated that “future AI progress will not come from making models bigger”, which represents how more development directions for openAI will be to make existing large models more useful and penetrate more scenarios.Nowadays, the AI big model is in a critical iteration period of rapid evolution from “usable” to “user-friendly”. How to infiltrate large models into various vertical scenarios, how to use large models at a lower cost, and how to expose more scenarios and users to AI have become the next focus of development. As AI moves towards practical scenarios, the importance of edge computing power becomes increasingly prominent. Edge computing power has natural advantages in cost, latency, and privacy, and can also serve as a bridge for preprocessing massive and complex requirements, guiding it towards large models. Kunqian has made efforts in the field of AI customization, with multiple GPU edge hardware, delving into thousands of application scenarios and accelerating AI applications.

Wenxiong Kang
South China University of Technology
Biography:Dr. Wenxiong Kang is currently a Professor with the School of Automation Science and Engineering & School of Future Technology at South China University of Technology, deputy director of Guangdong Province Intelligent Financial Enterprise Key Laboratory; and director of SCUT-BenLiu Power Artificial Intelligence Joint Laboratory. His research interests include biometric recognition and computer vision. In recent years, he has presided over more than 20 national key research and development projects and projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Guangdong Province,and he has published nearly 100 papers (more than 30 papers in JCR 1 journals) at prestigious international journals and conferences, of which 10 papers have won the Best Paper Award, the Distinguished Paper Award, and the Outstanding Paper Award. He has applied for more than 70 international and national invention patents and more than 40 were authorized, of which 16 patents have been successfully transferred to enterprises, and related techniques have been successfully applied to airports, power grids, and superstores and factories.
Speech Title:Application-Driven Vein Recognition
Abstract:In recent years, vein recognition has received extensive attention from the society due to its unique live body detection capability, and many progress have been made in vein image preprocessing, vein feature extraction and expression, etc. Especially on the existing public vein datasets, most recent work have been able to achieve good recognition performance, which has greatly facilitated the grounded application of finger vein recognition technology in a variety of occasions. This report focuses on the application-driven vein recognition research, and highlights the team’s vein recognition research work for different application scenarios, including: reflection-based imaging finger vein recognition for handheld devices, three-dimensional finger vein recognition for high-security situations, and on-the-fly palm vein recognition for unconstrained and weak-cooperative scenarios, and focuses on the research methodology, dataset construction, and prototype development.

Jianjun Qian
Nanjing University of Science and Technology
Biography:Dr. Qian is currently an Associate Professor with the School of Computer Science and Engineering at Nanjing University of Science and Technology. His research interests include pattern recognition, vision perception and biometrics. He has authored more than 80 papers in international journals and conferences such as IEEE TPAMI/TIP/TNNLS/TIM, IJCV, CVPR/ICCV/AAAI/IJCAI and other conferences many times. He has presided over three National Nature Science Founds, and participate key projects of NSFC many times. He has won two first prizes of Jiangsu Science and Technology Awards. He has been selected as Hong Kong Scholar, Outstanding Young Teacher of “Qinglan Project” in Jiangsu Province.
Speech Title:Robust Face Perception in Uncontrolled Scenarios
Abstract:Face robust perception plays an important role in real scene applications. However, face perception is still a challenging problem in non-controllable scenario due to illumination changes, large scale pose variations, small scale and occlusions. This report will introduce our recent research work from the aspects of robust face representation and face perception based physiological information measurement: (1) We provide an intrinsic analysis to reveal the working mechanism of softmax from the view of closeness and diversity. We find that enhancing the closeness of easy samples and preserving the diversity of hard samples can improve face representation robustness. (2) We leverage the short-term invariant prior of environment temperature to develop the dynamic group difference coding method for infrared face image, and further design the remote human body fever screening system.
Multi-modal Data Perception and Learning
Introduction
Multi-modal data is an information form similar to human perceptual learning and is easily obtainable in large quantities. Compared to unimodal data, the synchronicity of concepts across different modalities in these data provides supervised information for unlocking the latent explanatory factors of each modality. Traditional approaches to processing multi-modal data mainly focus on preserving the invariant factors within each modality while ignoring the other factors. This forum aims to explore artificial intelligence that achieves learning and thinking capabilities similar to humans through brain-like computation. It aims to promote research and development in multi-modal data perception learning, open up new problems, directions, and challenges in the field of pattern recognition, and provide an international platform for academic and industrial exchange, learning, and collaboration. At the same time, this forum has selected three highly influential papers published in Machine Intelligence Research (MIR), a Chinese journal also known as “机器智能研究” (abbreviated as MIR). The authors of these papers come from renowned research institutions and their teams both domestically and internationally, with the aim of bringing the latest progress and achievements to the conference attendees. On one hand, this promotes academic exchanges and discussions within the machine vision community, and on the other hand, it showcases the forward-thinking nature and impact of ICIG to a broader audience of MIR authors and readers. This workshop is supported by Technical Committee on Machine Vision.
Schedule
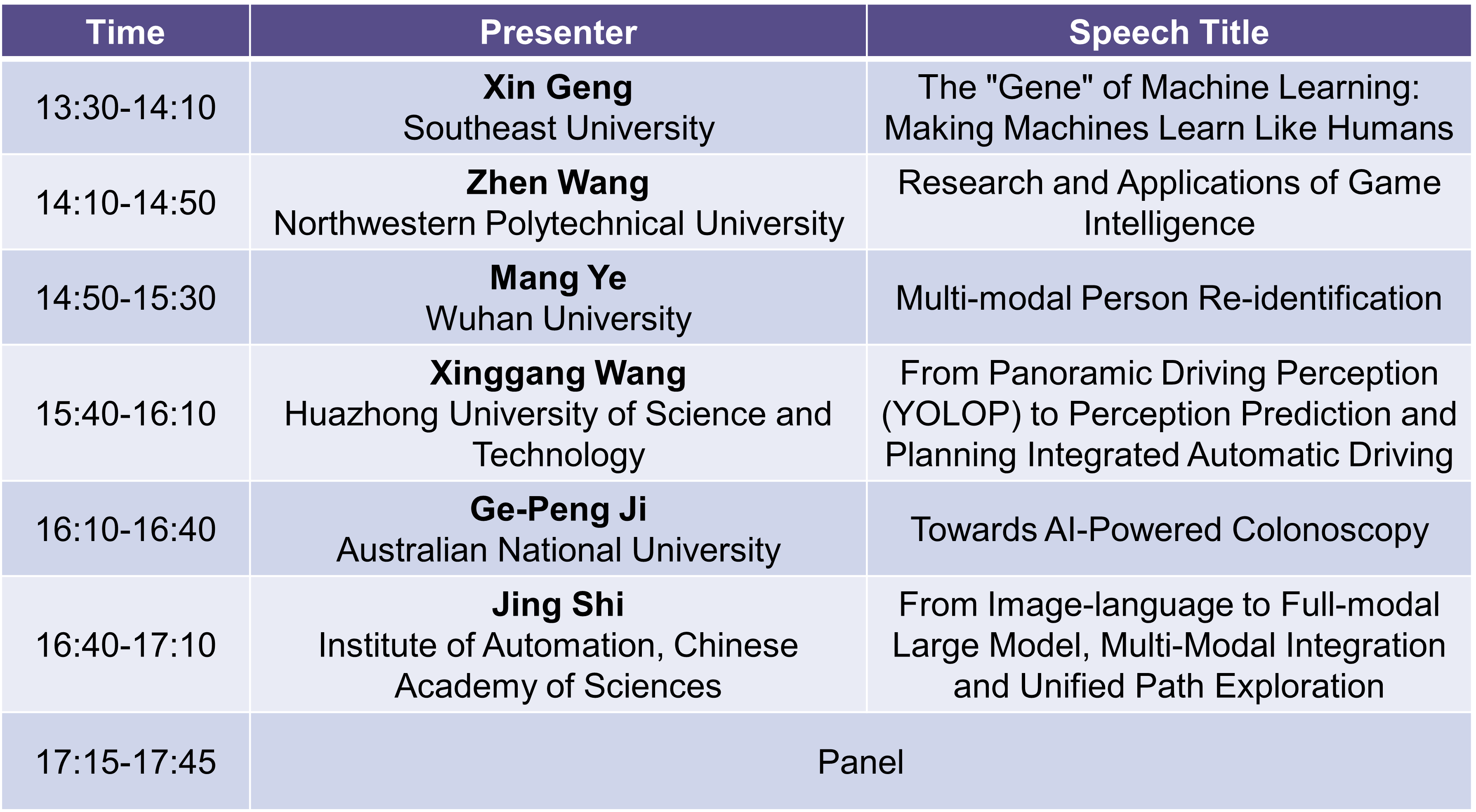
Sept. 22th 13:30-17:45
Organizers

Ming-Ming Cheng
Nankai University
Biography:Distinguished Professor of Nankai University, Head of Department of Computer Science. He presided over and undertook the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, the Science Fund for Outstanding Young Scholars, and major projects of the Ministry of Science and Technology. His main research direction is computer vision and computer graphics. He has published more than 100 academic papers (including more than 30 IEEE TPAMI papers) in SCI District 1/CCF Class A journals, with an h-index of 75 and 40,000 papers cited by Google. He has been cited more than 4,700 times for a single article, and has been selected as a global highly cited scientist and a Chinese highly cited scholar for many times. The technological achievements have been applied to the flagship products of Huawei, the National Disaster Reduction Center and other units. He has won 2 first prizes of the Natural Science Award of the Ministry of Education, 1 first prize of the Natural Science Award of the Chinese Society of Image and Graphics, and 1 second prize of the Natural Science Award of the Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence. Three doctoral students trained won provincial and ministerial excellent doctoral dissertation awards. He is currently the deputy secretary-general of the Chinese Society of Image and Graphics, the vice-chairman of the Tianjin Artificial Intelligence Society, and the editorial board member of IEEE TPAMI and IEEE TIP, a journal of SCI.

Guangwei Gao
Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Biography:In 2014, he received a Ph.D. degree in pattern recognition and intelligent systems, a national key discipline, from Nanjing University of Science and Technology. The research direction involves the perception and understanding of low-quality visual content. Currently presiding over the General Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Excellent Youth Fund Project of the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, and one high-level talent project of the “Six Talent Peaks” of Jiangsu Province, and participating in the key projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Science and Technology Innovation 2030-“New One major project of “Generation of Artificial Intelligence”. Served as a visiting researcher at the National Institute of Informatics of Japan (2019-2021). In recent years, he has published more than 70 papers in domestic and foreign core journals and important international conferences, including international authoritative journals IEEE TIP/TMM/TCSVT/TIFS/TITS, PR and authoritative conferences AAAI, IJCAI, etc.

Wanli Ouyang
Shanghai AI Laboratory
Biography:He used to be the director of research at the School of Electronic and Information Engineering, University of Sydney. In 2011, he received a Ph.D. from the Chinese University of Hong Kong. His research interests include pattern recognition, deep learning, computer vision, and AI for Science. Google Scholar has 30,000+ citations and an H-index of 79. In the industry-university-research circles, there are good scientific research resources and project cooperation, and the influence of scientific research is widely recognized in the industry. Published more than 160 papers in CCF Class A journals and conference papers such as TPAMI, JCV, CVPR, and NeurIPS. According to AlMiner, its influence in the field of computer vision ranks 50th in the world and 2nd in Australia. Received the Vice Chancellor’s award for “Outstanding Research” from the University of Sydney (Vice Chancellor’s award for “Outstanding Research”, only 2 people from the Faculty of Engineering of the University of Sydney won this award in the same year). According to the statistics of papers published in the field of computer vision and pattern recognition from 2016 to 2021 by Elsevier, an international authoritative organization, the average number of citations per article (Citations per paper) and field-weighted citation impact (FWCI) are both Australian. No. 1, top 10 in the world. Two articles were selected as the most influential articles of paperdigest CVPR/ICCV. He and his team won the first place in ImageNet and COCO object detection. ICCV Best Reviewer, IJCV and Pattern Recognition Editorial Board, TPAMI Guest Editor, ICCV2019 Exhibition Chair, CVPR2023 Senior Area Chair, CVPR2021, ICCV2021 Area Chair.

Huimin Lu
Kyushu Institute of Technology
Biography:Part-time professor at the Key Research and Development Center for IoT Intelligent Systems at Kyushu Institute of Technology, a national high-level talent. Research areas include artificial intelligence, robotics, and ocean observation. Serves as editor-in-chief for Computers & Electrical Engineering, Cognitive Robotics, Applied Soft Computing, Wireless Networks, IEEE Internet of Things Journal, IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, Pattern Recognition, ACM Trans on Internet Technology, and guest editor for other journals. Senior member of IEEE, Chairman of the IEEE Computer Society Big Data Technical Committee.
Presenters

Xin Geng
Southeast University
Biography:Executive Vice President of the Graduate School, winner of the National Outstanding Youth Fund and Excellent Youth Fund, and an outstanding member of the International Society of Engineering and Technology. His research interests include machine learning, pattern recognition, and computer vision. He has won many teaching and scientific research awards such as the second prize of the National Natural Science Award and the first prize of the National Teaching Achievement Award. He is currently a member of the Computer Discipline Appraisal Group of the Academic Degrees Committee of the State Council, a member of the Artificial Intelligence Expert Committee of the Computer Professional Teaching and Guidance Committee of the Ministry of Education, the vice chairman of the Jiangsu Computer Society, and a member of the Steering Committee of the Asia-Pacific International Conference on Artificial Intelligence.
Speech Title:The “Gene” of Machine Learning: Making Machines Learn Like Humans
Abstract:One of the fundamental driving forces behind this round of artificial intelligence boom is the development of modern machine learning, especially deep learning technology. Deep learning requires a lot of training data and computing resources. However, humans are often able to quickly learn a new concept from a small number of samples. This is because the brains of newborns are not random, and the result of thousands of years of human evolution has initialized the brains of newborns through genes. Inspired by this, we propose the “gene” of machine learning – Learngene. The new learning framework based on Learngene is expected to change the current rules of the game in the field of deep learning: now we only need to conduct large-scale training for open world tasks at a few “model suppliers”, and a “customer” for specific tasks only needs to learn from Purchase a Learngene from the “model supplier” to initialize your own lightweight model, and you can quickly adapt to your target task with a small number of samples, just like human learning.

Zhen Wang
Northwestern Polytechnical University
Biography:Secretary of the School of Cybersecurity, Executive Vice Dean of the National Institute of Confidentiality, Elected Member of The Academy of Europe, AAIA Fellow, globally highly cited scientist, National Distinguished Youth Scholar, Leader of Defense Innovation Team. His research interests include artificial intelligence, intelligent unmanned systems, and intelligent confrontation in cyberspace. He has published a series of achievements in Nature Communications, PNAS, Science Advance, Physical Review Letters, IEEE Transactions, IJCAI, AAAI, NeurIPS, ICML, ICLR, WWW, etc., with over 24,000 citations. The systems he developed have been deployed in multiple models. His accomplishments and deeds have been covered by major media outlets such as People’s Daily, Guangming Daily, Xinhua News Agency, Nature News, Live Science, Sciencedaily, and he has received commendations from the Northern Theater Command. He has delivered more than 80 keynote or invited speeches at international conferences, and has led more than 20 projects including key projects of the National Natural Science Foundation, overseas funds, and GF projects. He has received awards such as the Scientific Exploration Prize, China Youth May Fourth Medal, National Innovation Advancement Medal, National Labor Medal on May Day, the inaugural MIT-TR35 China (sole representative from the western region), and the first prize of the Ministry of Education, Shaanxi Province, Chinese Society of Aeronautics and Astronautics, and Chinese Institute of Electronics Science and Technology Award.
Speech Title:Research and Applications of Game Intelligence
Abstract:Game intelligence is an intersecting field covering game theory, artificial intelligence, etc. It focuses on the study of interactions between individuals or organizations, and how to achieve accurate solutions to optimal strategies through quantitative modeling of game relationships, ultimately forming an intelligent Decision-making and decision-making knowledge base. In recent years, with the massive explosion of behavioral data and the diversification of game forms, game intelligence has attracted the research interest of more and more scholars and has been widely used in real life. We will focus on game intelligence This research field has been systematically investigated from three aspects. First, the relevant background of game intelligence is reviewed, covering the single-agent Markov decision-making process, multi-agent modeling technology based on game theory, and reinforcement learning. , multi-agent solution solutions such as game learning. Secondly, according to the different game relationships between agents, the game is divided into three major paradigms: cooperative game, confrontational game and mixed game, and the characteristics of each game intelligence paradigm are introduced respectively. Main research questions, mainstream research methods and current typical applications. Finally, it summarizes the current research status of game intelligence, as well as the main problems and research challenges that need to be solved, and gives future prospects for academia and industry to further promote the national artificial intelligence development strategy.

Mang Ye
Wuhan University
Biography:Mang Ye is currently a Full Professor at the School of Computer Science, Wuhan University. He received the PhD degree from Hong Kong Baptist University in 2019, supported by Hong Kong PhD Fellowship. He received the B.Sc and M.Sc degrees from Wuhan University in 2013 and 2016. He worked as a Research Scientist at Inception Institute of Artificial Intelligence and worked as a Visiting Scholar at Columbia University. He has published more than 80 papers, including 40+ CCF-A papers as the first/corresponding author. He received 5500+ citations, including those from 2 Turing awardees (Geoffrey Hinton and Yann Lecun). Ten papers are ESI Highly Cited. He received the National Science Foundation of China (NSFC) Excellent Youth Fund (Overseas). His research interests include open-world visual learning and its applications in multimedia analysis and reasoning.
Speech Title:Multi-modal Person Re-identification
Abstract:Person re-identification has achieved inspiring performance in single-modality RGB scenarios. However, in complex real-world environments, relying solely on a single modality has certain limitations and struggles to effectively handle diverse scene variations. Practical applications of person re-identification may require the integration of various modalities of data, including visible images/videos, infrared images, sketch images, text, sound, and others. In this talk, I will firstly provide a brief introduction to several common cross-modal person re-identification tasks, presenting the research background and challenges. Secondly, I will introduce the research progress of our team in the field of multi-modal person re-identification, including sketch-to-photo, text-to-image, infrared-to-visible, etc. Finally, some future research directions on this topic will be discussed.

Xinggang Wang
Huazhong University of Science and Technology
Biography:Professor of the School of Telecommunications, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, National Top-notch Young Talents Program, co-editor-in-chief of Image and Vision Computing journal. Published more than 60 academic papers in international top journal conferences, Google cited more than 20,000 times, and the highest single paper cited more than 2,100 times. He serves as the field chair of CVPR 2022, ICCV 2023, and CVPR 2024, and serves as the editorial board member of journals such as Pattern Recognition. Selected into the Young Talents Project of the China Association for Science and Technology, won the Hubei Youth May 4th Medal, CSIG Young Scientist Award, Wu Wenjun Artificial Intelligence Outstanding Youth Award, CVMJ 2021 Best Paper Award, Hubei Provincial Natural Science Second Prize, etc., and guided students to win the 2022 Natural Science Award The National “Internet +” Competition Gold Award.
Speech Title:From Panoramic Driving Perception (YOLOP) to Perception Prediction and Planning Integrated Automatic Driving
Abstract:This report will present the Single-stage Panoramic Driving Perception (YOLOP) method developed by our research group, which has been published in the journal “Machine Intelligence Research”. It analyzes how to efficiently perform joint optimization of tasks such as object detection, drivable area segmentation, and lane detection in autonomous driving perception, as well as its real-time deployment on embedded AI chips. Furthermore, it will discuss how our research group achieves accurate 3D object detection, object trajectory prediction, and self-vehicle trajectory planning based on omni-directional cameras, Transformers, and Query mechanisms for complex dynamic traffic scenarios. This aims to enhance the accuracy of perception, prediction, and planning integration in autonomous driving, while maintaining a concise framework.

Ge-Peng Ji
Australian National University
Biography:A doctoral student at the Australian National University. He graduated from Wuhan University in 2021 with a master’s degree. His main research directions include medical image analysis, complex visual scene understanding, video content analysis and other technologies. He has more than 10 papers in TPAMI, TMI, CVPR, ICCV, MICCAI, and has been invited to serve as a reviewer for several top computer vision journals and conferences, and has been cited by Google Scholar more than 2,000 times. He has worked as a research intern in Yuanyuan Artificial Intelligence Research Institute, Alibaba and other companies.
Speech Title:Towards AI-Powered Colonoscopy
Abstract:As the third largest cancer group in the world, colorectal cancer has gradually evolved into the second leading cause of malignant death in industrialized countries, seriously threatening human life and health. Most colorectal cancers are evolved from adenomatous polyps. If precancerous lesions can be detected and removed through early colonoscopy, the incidence rate can be greatly reduced by about 30%, effectively preventing the occurrence and development of colorectal cancer . Therefore, endoscopists can accurately find and judge the area of polyps through optical diagnosis during examination, which will avoid unnecessary surgical resection and pathological examination, and improve the cost-benefit ratio of colonoscopy screening. In recent years, with the vigorous development of artificial intelligence technology, what kind of sparks will it create with traditional colonoscopy screening technology? With the theme of AI-driven colonoscopy screening technology, this report introduces the origin of the problems, challenges, and technical solutions of colonoscopy screening technology, and discusses potential future research directions.

Jing Shi
Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Biography:Assistant Professor at the Institute of Automation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, a specially-appointed research backbone, and a core algorithm developer for the full-modal large model of “Zidong Taichu”. Visiting scholar at the Center for Language and Speech Processing (CLSP) at Johns Hopkins University, and the co-professor is Professor Shinji Watanabe, a well-known scholar in the field of speech. One of the maintainers of ESPnet, an end-to-end NLP/Speech open source popular framework. He has published more than 20 papers in top international journal conferences, and his research direction is multi-modal human-computer interaction and speech processing.
Speech Title: From Image-language to Full-modal Large Model, Multi-Modal Integration and Unified Path Exploration
Abstract:In this report, we will present an overview of vision-language pre-training based on the article “VLP: A Survey on Vision-Language Pre-training” published by our research team in the journal “Machine Intelligence Research”. We will discuss the overall summary of vision-language multi-modal pre-training from various aspects including feature extraction, feature representation, model architecture, pre-training objectives, datasets, downstream tasks, and existing representative works. Furthermore, we will expand the typical binary multi-modalities of vision and language to report on unified cognitive interaction models that encompass more modalities such as images, speech, and videos. We will explore the current state-of-the-art architectures, technical approaches, and challenges faced in supporting full modality in large-scale pre-training models for vision-language integration.
Progress in Frontier Research of 3D Vision
Introduction
Three-dimensional (3D) vision is an essential research field within computer vision, encompassing a broad variety of topics, including depth imaging, 3D reconstruction, 3D object detection and recognition, as well as 3D scene understanding and content generation. In recent years, with the rapid development of 3D vision technology, the achievements in this domain have found extensive applications in intelligent systems such as autonomous vehicles, robotics, as well as content generation services.
The purpose of this forum is to bring together professionals engaged in 3D vision research from various fields, including computer vision, computer graphics, and robotics for facilitating the sharing of the latest technological developments in 3D vision, exploring the practical applications of 3D vision in different domains, and analyzing the challenges, difficulties, and potential opportunities encountered in 3D vision research. In general, this forum aims to provide a platform for experts, scholars, and practitioners in the field of 3D vision, both domestically and internationally, to exchange ideas and foster collaboration. This workshop is supported by Technical Committee on 3D Vision.
Schedule
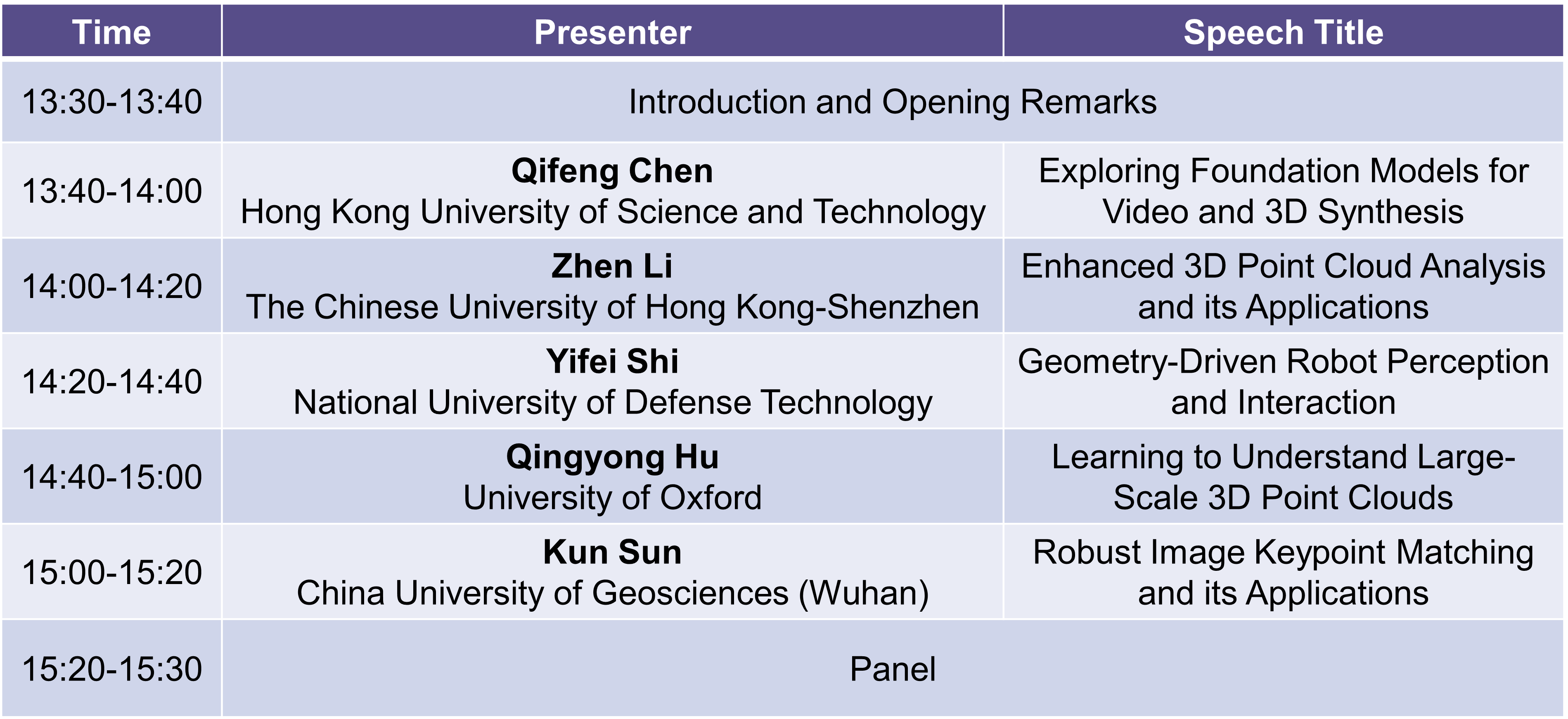
Sept. 22th 13:30-15:30
Organizers

Baoquan Chen
Peking University
Biography:Baoquan Chen is a Professor of Peking University, where he is the Associate Dean of the School of Artificial Intelligence. His research interests generally lie in computer graphics, computer vision, visualization, and human-computer interaction. He has published more than 200 papers in international journals and conferences, including 40+ papers in ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)/SIGGRAPH/SIGGRAPH_ Asia. Chen serves/served as associate editor of ACM TOG/IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Graphics (TVCG), and has served as conference steering committee member (ACM SIGGRAPH Asia, IEEE VIZ), conference chair (SIGGRAPH Asia 2014, IEEE Visualization 2005), program chair (IEEE Visualization 2004), as well as program committee member of almost all conferences in the visualization and computer graphics fields for numerous times. Chen is the recipient of 2002 Microsoft Innovation Excellence Program, 2003 NSF CAREER award, 2004 McKnight Land-Grant Professorship at the University of Minnesota (Twin Cities), 2005 IEEE Visualization Best Paper Award, and 2014 Outstanding Achievement Award of Chinagraph.
Prior to the current post, he was dean of the School of Computer Science and Technology and the School of Software and founding director of the Interdisciplinary Research Center, Shandong University (2013-2018), founding director of the Visual Computing Research Center and deputy director of the Institute of Advanced Computing and Digital Engineering, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology (SIAT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (2008-2013), and a faculty member at the department of Computer Science and Engineering at the University of Minnesota at Twin Cities (2000-2008). Chen received an MS in Electronic Engineering from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, and a second MS and then PhD in Computer Science from the State University of New York at Stony Brook, New York, U.S.A. For his contribution to spatial data visualization, he was elected IEEE Fellow in 2020. He was inducted to IEEE Visualization Academy and was elected as CSIG Fellow in 2021.
Presenters

Qifeng Chen
Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
Biography:Qifeng Chen is an assistant professor in CSE and ECE at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology. He received his Ph.D. in computer science from Stanford University in 2017. His research interests are image synthesis, computational photography, and autonomous driving. He was named one of 35 Innovators under 35 in China by MIT Technology Review and received the Google Faculty Research Award. He has served as an area chair for CVPR and NeurIPS. He won 2nd place worldwide at the ACM-ICPC World Finals and a gold medal in IOI.
Speech Title:Exploring Foundation Models for Video and 3D Synthesis
Abstract:Recent generative AI technologies have transformed the paradigm in visual content creation and editing, which can generate photorealistic images in the wild based on text-to-image foundation models. However, video and 3D synthesis are yet to achieve the same visual quality as image synthesis. In this talk, I will share our recent research on video and 3D synthesis with foundation models, which includes creating a text-to-video foundation model, efficient text-guided video editing, 3D scene generation, and personalized 3D avatar generation. I will share the experiences of how we address the challenges in generative AI research, which is computation-demanding, data-hungry, and under accelerated development.

Zhen Li
The Chinese University of Hong Kong-Shenzhen
Biography:Dr. Zhen Li is currently an assistant professor at the School of Science and Engineering (SSE) of The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen/Future Intelligent Network Research Institute (FNii) of The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen. He is also a research scientist at the Shenzhen Institute of Big Data (SRIBD) and a special researcher at the South China Hospital Affiliated to Shenzhen University. Dr. Li Zhen was selected for the 2021-2023 Seventh China Association for Science and Technology Young Talent Support Project. Dr. Zhen Li received his PhD in Computer Science from the University of Hong Kong (2014-2018), a MS in Communication and Information Systems from Sun Yat-Sen University (2011-2014), and a BS in Automation from Sun Yat-Sen University (2007-2011). He was also a visiting scholar at the University of Chicago in 2018 and a visiting student at the Toyota Technical Institute (TTIC) in Chicago in 2016. His research interests include interdisciplinary research in artificial intelligence, 3D vision, computer vision, and deep learning-assisted medical big data analysis. He has published more than 30 papers in top conferences and journals, such as top journals Cell Systems and Nature Communications, IEEE TNNLS, IEEE TMI, PLOS CB, etc. and top conferences CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, AAAI, IJCAI, ACL, ECAI, MICCAI, RECOMB, ISBI, etc.
Meanwhile, Dr. Zhen Li is the contact map prediction champion in the Olympiad in protein structure prediction (CASP12) and serves as the baseline method for the DeepMind team’s AlphaFold first version. The corresponding paper has won the PLOS CB Breakthrough and Innovation Award (one per year) and is a highly cited paper in Web of Science. As a mentor, Dr. Li Zhen led the students to win the SemanticKITTI championship in the large-scale point cloud analysis competition, the second place in the ICCV2021 large-scale urban street scene understanding competition, and the first place in the IEEE ICDM Global A.I. Weather Challenge (out of 1700 teams). Finally, Dr. Li Zhen also received scientific research funding from national, provincial, municipal and industrial circles.
Speech Title:Enhanced 3D Point Cloud Analysis and its Applications
Abstract:Point clouds, as a fundamental 3D representation form, have found applications in various tasks such as autonomous driving, robot perception, and biomolecular structure prediction and design. Despite significant advancements in 3D point cloud analysis in recent years, algorithms for processing large-scale point clouds remain a focal point of research due to their massive data volume, unordered nature, lack of texture, and sparse features.
This report starts with the acquisition of point clouds and introduces a novel approach based on reversible networks for point cloud down-sampling and reconstruction, greatly improving the storage and communication efficiency of large-scale point cloud data. With effective point cloud data at hand, we then delve into classic tasks such as shape classification, 3D detection and tracking of point clouds, and semantic segmentation of large-scale 3D scenes. Our research spans from single-modal to multi-modal fusion and distillation techniques, and our algorithms have demonstrated outstanding performance in numerous public competitions, including first place in the SemanticKitti semantic segmentation challenge, first place in the CVPR2023 HOI4D segmentation challenge, second place in the ICCV21 Urban 3D competition, third place in the NuScenes semantic segmentation challenge, among others.
Finally, we extend our point cloud analysis algorithms to downstream applications, such as visual reasoning of 3D scenes, 3D scene description generation, AI-generated anchor faces for broadcasters, prediction of protein-small molecule binding, and binding site prediction, showcasing the versatility and broad impact of our research.

Yifei Shi
National University of Defense Technology
Biography:Yifei Shi is an Associate Professor at the College of Intelligence Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology (NUDT). He received his Ph.D. degree in computer science from NUDT. He was a visiting student research collaborator at Princeton University. His research interests mainly include 3D vision, computer graphics, and intelligent robots. He has published 30+ papers in top-tier journals and conferences, including IEEE T-PAMI、ACM TOG、SIGGRAPH、CVPR、ICCV、ECCV (Oral).
Speech Title:Geometry-Driven Robot Perception and Interaction
Abstract:3D vision is at the core of intelligent robot perception and interaction. Existing methods learn experience and knowledge directly from data, which suffer from lack of structural information, low precision and poor stability. To address this issue, we study methods for learning from 3D data with embedded geometric structure priors. In robot perception, we propose a learning-based 3D object symmetry detection method, achieving accurate symmetry detection and generalization on untrained objects. In robot interaction, we apply object symmetry and stacking scene structure analysis to robot grasping, improving the accuracy and reliability of grasping detection and planning.

Qingyong Hu
University of Oxford
Biography:Qingyong Hu is a Ph.D. in the Cyber-Physical System (CPS) research group of Department of Computer Science at the University of Oxford, supervised by Niki Trigoni, Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering in the UK, and Professor Andrew Markham from Oxford University. His research interests lie in 3D computer vision, particularly in the semantic understanding of large-scale 3D point clouds, instance segmentation, and registration. He has published several papers in journals and international conferences including IEEE TPAMI/IJCV/CVPR/NeurIPS. His papers have been cited by 3400+ times (Google Scholar), and the RandLA-Net paper has also been listed as the most influential paper in CVPR 2020 (PaperDigest). Additionally, he also chaired 2 International Workshops (Urban3D) at ICCV’21 and ECCV’22. He was fortunately awarded the Huawei UK AI Fellowship during 2021-2023, and received the World Artificial Intelligence Conference Youth Outstanding Paper Award, the outstanding student reviewer of ICCV 2021 (top 5%), and the Grand Prize and First Place in the 11th Chinese Graduate Electronic Design Competition (1/1400).
Speech Title:Learning to Understand Large-Scale 3D Point Clouds
Abstract:Giving machines the ability to precisely perceive and understand the 3D visual world is the fundamental step to allow them to interact competently within our physical world. However, the research on large-scale 3D scene understanding and perception is still in its infancy, due to the complex geometrical structure of 3D shapes and limited high-quality data resources. This presentation will proceed from three aspects: data, efficiency, and learning in large-scale 3D point cloud semantic understanding, to systematically review and introduce the relevant research I engaged in during my doctoral period.

Kun Sun
China University of Geosciences (Wuhan)
Biography:Kun Sun received his PhD from School of Artificial Intelligence and Automation, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, under the supervision of Prof. Wenbing Tao. He is now working as an associate professor at School of Computer Science, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan). His research interests are multi-view image matching, large scale Structure from Motion (SfM), 3D point cloud processing. He has published over 30 publications on conferences and journals including CVPR, AAAI, ICME, T-PAMI, TIP, TMM, Information Fusion and Information Sciences. He is a member of the CSIG Technical Committee on 3D Vision (CSIG-3DV).
Speech Title:Robust Image Keypoint Matching and its Applications
Abstract:Finding matching pixels between two images captured at different views plays an important role in many 3D related vision tasks, such as panorama imaging, vision-based localization and structure from motion. However, due to variances such as viewpoint, illumination, texture, occlusion, rotation and scaling, finding robust correspondences that are friendly to downstream tasks still remains a challenging task. In this presentation, I will introduce some of my studies in image matching, descriptor learning and large-scale 3D reconstruction.
Opportunities and Security Challenges of Large Visual Model
Introduction
In the past few months, the large AI models like ChatGPT have shown an astonishing level of general intelligence, and have set off a research wave of large models in various application fields. In the filed of computer vision, various large visual models like SAM have also emerged in endlessly. They not only perform well in classic visual tasks such as image segmentation and image generation, but also show amazing potential in various complex visual understanding tasks. AI large models bring in new opportunities for further breakthroughs of computer vision. Meanwhile, preliminary research in the community has found that the security and privacy issues commonly existed in regular AI models also exist in large visual models, and even more complex and may bring in more severe security threats.
The current development of large visual models is still in its infancy. It is necessary to deeply explore the opportunities and the security challenges of large visual models. Therefore, this forum will invite well-known experts in the community to share the latest scientific research on large visual models, and conduct in-depth discussions on related security challenges. We hope to attract more researchers’ attention, and work together with the research community to promote the rapid and healthy development of computer vision. This workshop is supported by The School of Data Science, Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-Shenzhen), Institute of Artificial Intelligence,
Beihang University and Huawei 2012 Shield Lab.
Schedule
Sept. 22th 13:30-15:30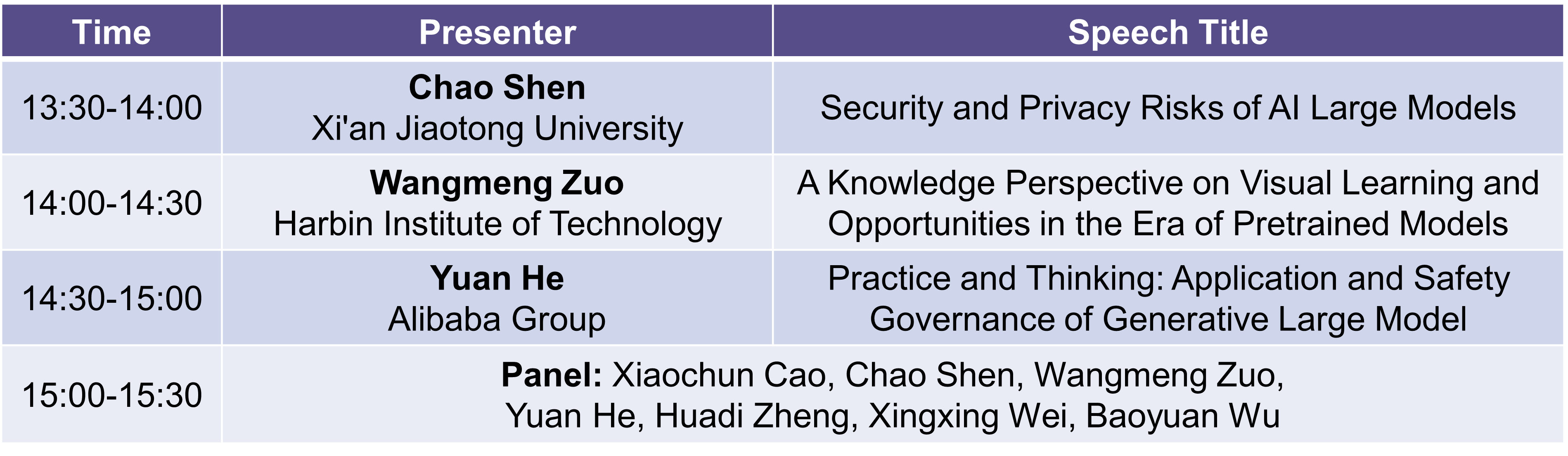
Organizers

Baoyuan Wu
The Chinese University of Hong Kong – Shenzhen
Biography:Dr. Baoyuan Wu is an Associate Professor of School of Data Science, the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (CUHK-Shenzhen). His research interests are AI security and privacy, machine learning, computer vision and optimization. He has published 70+ top-tier conference and journal papers, including TPAMI, IJCV, NeurIPS, ICML, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, ICLR, AAAI, and one paper was selected as the Best Paper Finalist of CVPR 2019. He is currently serving as an Associate Editor of Neurocomputing, Organizing Chair of PRCV 2022, Area Chair of CVPR 2024, NeurIPS 2022/2023, NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks Track 2023, ICLR 2022/2023/2024, ICML 2023, AAAI 2022/2024, AISTATS 2024, and Deputy Secretary-General of the professional committee of CAA-PRMI. He was selected into the 2021 and 2022 World’s Top 2% Scientists List released by Stanford University.

Xingxing Wei
Beihang University
Biography:
Wei Xingxing, Ph.D., is an associate professor and doctoral supervisor at the Institute of Artificial Intelligence, Beihang University. He was awarded the title of Young Elite Talent at Beihang University. From 2017 to 2019, he conducted postdoctoral research at the Department of Computer Science, Tsinghua University. Prior to that, he obtained his bachelor’s and doctoral degrees from Beihang University and Tianjin University respectively. After graduation, he worked as a senior algorithm engineer in computer vision at Alibaba Group.
His main research interests lie in adversarial machine learning and computer vision. He has published over 30 academic papers in top conferences and journals in the field of artificial intelligence, including CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, IJCAI, AAAI, ACMMM, TCYB, TMM, and TGRS. He and his team won the championship in the CAAD CTF, an international evaluation competition for adversarial samples, hosted by DEFCON2018. He also guided students to achieve the second place in the robust logo detection competition at ACMMM2021 and the fourth place in the ImageNet unrestricted adversarial attack competition at CVPR2021. He has been invited multiple times to serve as a committee member for top international conferences in the field of artificial intelligence.
As a project leader, he has undertaken several projects, including the “New Generation Artificial Intelligence” 2030 major project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) general and youth projects, the special funding and general projects of the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, the CCF-Tencent Rhino Bird Fund, as well as several horizontal projects from well-known companies such as Huawei, Tencent, and Alibaba.
Co-organizers

Xiaochun Cao
Sun Yat-sen University, Shenzhen Campus
Biography:Xiaochun Cao is a Professor and Dean of School of Cyber Science and Technology, Shenzhen Campus of Sun Yat-sen University. He is also a recipient of the National Distinguished Youth/Outstanding Youth Fund. He mainly engages in fundamental research in artificial intelligence and applied research in content security in cyberspace.
Presenters

Chao Shen
Xi’an Jiaotong University
Biography:Chao Shen is a full Professor of the Department of Electronics and Informatics, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Director of the University Talent Office, Head of the Innovation Team of the Ministry of Education, and the winner of Alibaba DAMO Academy Award, MIT TR35 China, and Fok Yingdong Young Teacher First Prize. He mainly engages in the research of trustworthy artificial intelligence, intelligent software testing, intelligent system security and control, and has published more than 100 academic papers. He has won 3 provincial and ministerial science and technology awards. He has presided over more than 20 projects of the NSF Outstanding Youth Science Foundation, the NSFC Key Project, the NSFC International (Regional) Cooperation Project, the National key R&D plans and enterprise projects, authorized/accepted more than 50 invention patents, and presided over/participated in the formulation of 4 international/industry/group standards. He serves as the editorial board member of 9 international journals including IEEE TDSC, and the deputy director of the Organization Working Committee of the Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence.
Speech Title:Security and Privacy Risks of AI Large Models
Abstract:In recent years, large model technology led by GPT has opened a new era of AI research. However, attackers may take advantage of the vulnerability of large models to carry out illegal activities such as identity forgery, telecom fraud, and secret theft, which poses a serious threat to personal security, social security, and even national security. Thus, studying and analyzing the security and privacy risks of large models is of great significance and needs to be solved urgently.
From the three perspectives of confidentiality, integrity and privacy of large models, this report will analyze various challenges of AI security and privacy in the era of large models, and discuss hot research issues such as privacy leakage, model theft, adversarial attacks, backdoor threats, output security, fairness and bias of large models. This report aims to discover and analyze the security and privacy risks of large models, and promote the development of AI large model.

Wangmeng Zuo
Harbin Institute of Technology
Biography:Wangmeng Zuo is currently a Professor in the School of Computer Science and Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology. His research interests include low level vision, image/video generation, and multi-modality learning. He has published over 100 papers in top-tier academic journals and conferences. He was also served as Area Chairs of ICCV 2019, CVPR 2020/2021/2024, a Tutorial Organizer in ECCV 2016, and a program co-chair of ECCV workshop on AIM 2020. He is also served as an associate editor of IEEE T-IP and IEEE T-PAMI.
Speech Title: A Knowledge Perspective on Visual Learning and Opportunities in the Era of Pretrained Models
Abstract:In recent years, with the emergence of multimodal pre-training models such as CLIP and Stable Diffusion, how to fully utilize large pre-trained models for efficient tuning in various downstream tasks has become a hot research topic and trend in computer vision. In this talk, we will first present a survey on visual learning from the knowledge perspective. Then we discuss the possible forms of knowledge in the era of pretrained models, and their potential applications in efficient visual learning.

Yuan He
Alibaba Group
Biography:Dr. Yuan He is a Senior Staff Engineer at Alibaba Group. He received his B.E. and Ph.D. degrees from Tsinghua University. Currently his works mainly focus on content moderation, intellectual property protection and AI safety. His research areas include machine learning, pattern recognition, computer vision and AI safety. Dr. He is the author of more than 70 journal and conference articles, such as TPAMI, ICML, CVPR, ICCV and NeurIPS. He is also the inventor of more than 30 patents filed in China, Europe and US. In recent years, he served as the organizer or PC member of workshops and challenges related to adversarial examples and model robustness on several international conferences, such as the IJCAI 2019 workshop on Artificial Intelligence for Business Security (AIBS) and the CVPR 2021 workshop on Adversarial Machine Learning in Real-World Computer Vision Systems and Online Challenges (AML-CV). He is also the spec editor of IEEE and CCSA AI Robustness standards.
Speech Title:Practice and Thinking: Application and Safety Governance of Generative Large Model
Abstract:Recently, generative AI represented by large language models (LLMs) has developed by leaps and bounds, bringing a new wave of intelligent applications and leading us towards general artificial intelligence. Generative AI of vision has brought great opportunities for the applications of image and video content generation, but also brought greater challenges to the ethical governance of artificial intelligence. Compared with traditional artificial intelligence security governance, large generative models governance faces many problems such as generative quality and content controllability, possibility of technology abuse, data privacy protection, and ethical alignment. Therefore, application providers based on large generative models need to provide systematic security management measures. This talk will introduce our technological innovation and system practice in both the application and safety governance of large generative models.
Image Perception and Its Oceanic Applications
Introduction
Visual information processing aims to realize intelligent processing, analysis and understanding of visual information such as images and videos through machine learning, computer vision and other technologies. It is a key technology in the field of artificial intelligence and Internet of Things. The report of 20th National Congress on “developing marine economy, protecting marine ecosystems, and accelerating the construction of a strong marine country” has further clarified the new direction of visual information processing technology. In this context, it is of great significance to discuss the optimization and application of visual information processing technology in the background of “intelligent ocean”. With the theme of visual information perception and featuring its application in the ocean, this workshop invites experts in related fields to discuss the focal issues of visual information quality perception, underwater imaging and compression around this theme. It provides a platform for scholars and postgraduates who are interested in research on visual information processing and ocean signal analysis to interact and exchange ideas. This workshop is supported by Technical Committee on Image and Video Communications.
Schedule
Sept. 22th 13:30-15:30
Organizers

Tiesong Zhao
Fuzhou University
Biography:Tiesong Zhao received the B.S. degree in electrical engineering from the University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China, in 2006, and the Ph.D. degree in computer science from the City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, in 2011. He served as a Research Associate with the Department of Computer Science, City University of Hong Kong (2011-2012), a Postdoctoral Fellow with the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Waterloo (2012-2013), and a Research Scientist with the Ubiquitous Multimedia Laboratory, The State University of New York at Buffalo (2014-2015). He is currently a Minjiang Distinguished
Professor in the College of Physics and Information Engineering, Fuzhou University, China. His research interests include multimedia signal processing, coding, quality assessment, and transmission. Due to his contributions in video coding and transmission, he received the Fujian Science and Technology Award for Young Scholars in 2017. He has also been serving as an Associate Editor of IET Electronics Letters since 2019.

Weiling Chen
Fuzhou University
Biography:Weiling Chen received the B.S. and Ph.D. degrees in communication engineering from Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, in 2013 and 2018, respectively. She is currently a Associate Professor with the Fujian key lab for intelligent processing and wireless transmission of media information, Fuzhou University, China. From Sep. 2016 to Dec. 2016, she was visiting at the School of Computer Science and Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore. Her current research interests include image quality perception, computer vision and underwater acoustic transmission.
Presenters

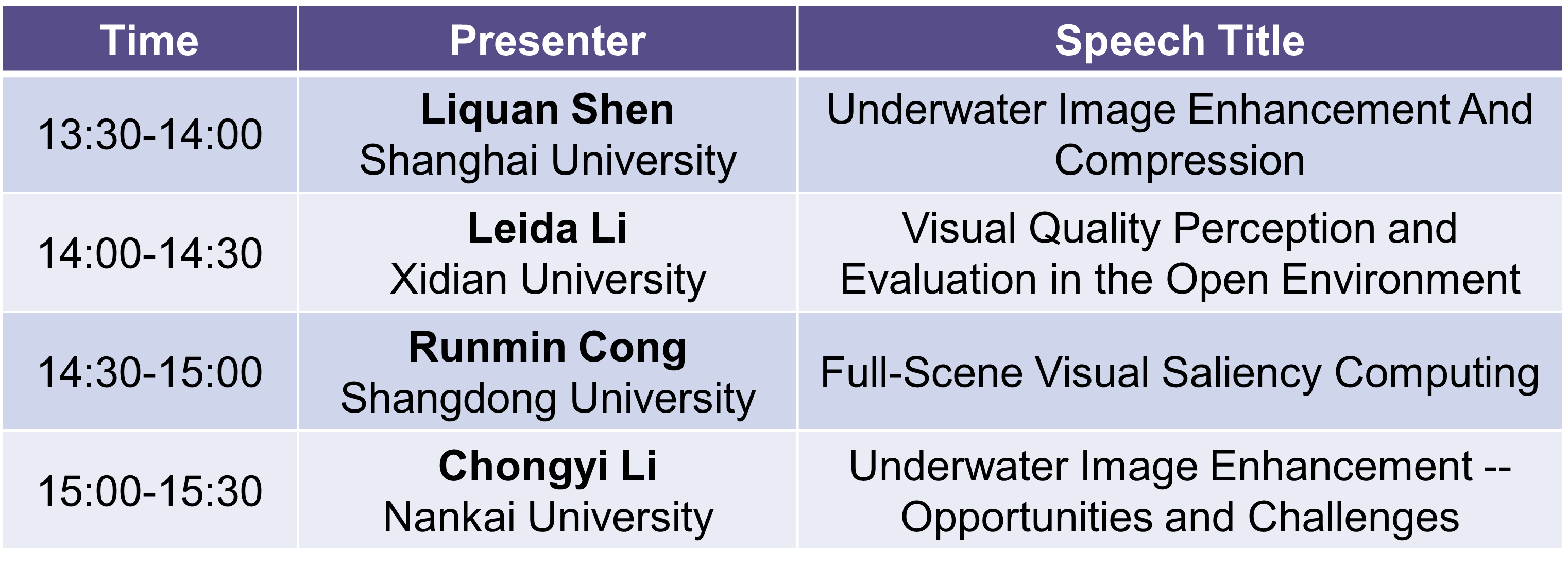
Liquan Shen
Shanghai University
Biography:Liquan Shen is with the Faculty of the School of Communication and Information Engineering, Shanghai University, where he is currently a Professor. He has authored or coauthored more than 100 refereed technical papers in international journals and conference proceedings, such as IEEE T-PAMI, IEEEE T-IP, IEEE T-CSVT, IEEE T-MM, IEEE T-GRS, ICCV, AAAI, IJCAI. His research interests include underwater imaging, video coding, video quality assessment and 3DTV.
Speech Title:Underwater Image Enhancement and Compression
Abstract:As a direct and effective method to obtain Marine information, underwater imaging has advantages of small disturbance to underwater environment and large observation area compared with other exploration technologies and its development has attracted much attention. Due to scattering and absorption of light transmission in water, underwater images have low contrast, low definition, color distortion and other problems. Meanwhile, the bandwidth of underwater acoustic wireless transmission is only about 15-30kbit/s, which is difficult to achieve high rate data transmission by existing methods. Core technologies such as underwater image quality enhancement and compression will play an increasingly important role in future marine exploration. The content of this report mainly includes the following aspects: (1) underwater image quality assessment database for machine measurement and human vision; (2) underwater image enhancement for machine measurement; (3) underwater image enhancement for human vision; (4) underwater image enhancement with artificial light; (5) underwater image compression.

Leida Li
Xidian University
Biography:Leida Li received the B.Sc. and Ph.D. degrees from Xidian University in 2004 and 2009, respectively. From 2014 to 2015, he was a Research Fellow with the Rapid-rich Object SEarch (ROSE) Lab, Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore, where he was a Senior Research Fellow from 2016 to 2017. Currently, he is a Full Professor with the School of Artificial Intelligence, Xidian University, China. His research interests include image/video quality evaluation, computational aesthetics and visual emotion analysis. His research is funded by NSFC, OPPO, Huawei and Tencent, etc. He has published more than 100 papers in these areas. He is on the editor board of Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation (Best Associate Editor Award 2021), EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing and Journal of Image and Graphics (Excellent Editor Award 2022). He is a senior member of CCF and CSIG.
Speech Title:Visual Quality Perception and Evaluation in the Open Environment
Abstract:Visual quality evaluation has important applications in many fields, such as the design of imaging systems, optimization of image and video processing algorithms, and image big data screening, and has received extensive attention in recent years. However, the existing visual quality evaluation models are typically built based on deep networks and limited training data, which carries a significant risk of overfitting. Therefore, it is extremely challenging for these models to deal with visual quality perception and evaluation task in the open environment. To address the above issues, the talk will focus on exploring visual quality perception and evaluation for open environments, including image quality evaluation and video quality evaluation, focusing on the model generalization. Specifically, I will detail the latest research progress and open problems from multiple perspectives, such as transfer learning, domain adaptation, domain generalization, as well as model pre-training.

Runmin Cong
Shangdong University
Biography:Runmin Cong (IEEE/CCF/CSIG/CIE Senior Member, ACM/APSIPA IVM Member) is currently a Professor with the School of Control Science and Engineering, Shandong University (SDU), Jinan, China. His research interests include computer vision, machine learning, multimedia processing and understanding, saliency computation, remote sensing image interpretation and analysis, and visual content enhancement in an open environment, etc. He has published more than 70 papers in prestigious international journals and conferences, including 57 IEEE/ACM Trans/CCF-A papers, 2 ESI hot papers, 12 ESI highly cited papers, and 16 China patents have been authorized. He serves/served as an Associate Editor/Editorial Board Member of the Neurocomputing, the IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, and the AC/SPC/PC of NeurIPS, CVPR, ICML, ICCV, ECCV, SIGGRAPH, ACM MM, AAAI, IJCAI, etc. Dr. Cong was a recipient of the Young Elite Scientist Sponsorship Program by the China Association for Science and Technology, the Beijing Nova Program, the The World’s Top 2% Scientists (2020, 2021), IEEE ICME Best Student Paper Award Runner-Up, First Prize for Scientific and Technological Progress Award of Tianjin Municipality, ACM SIGWEB China Rising Star Award, Excellent Doctorial Dissertation Award from CSIG and BSIG, Excellent Scientific Paper Award for Beijing Youth.
Speech Title:Full-Scene Visual Saliency Computing
Abstract:Inspired by human visual attention mechanisms, the goal of visual saliency detection is to extract the most conspicuous regions or objects from the given input data. It has been widely applied to research fields including object tracking, content editing,
compression coding, quality assessment, as well as engineering applications like smart photography, smart healthcare, autonomous driving, and earth observation. The big data era has not only brought a huge increase in the quantity of data, but also breakthroughs in the quality of data. With the development of imaging devices and hardware technologies, diverse types of data across different modalities, spaces, and dimensions are emerging, providing rich data resources for better understanding the objective world, while also bringing new challenges. With visual saliency detection as the basic task, this report will introduce our work on cross-modal saliency detection, saliency detection on associative data, and remote sensing saliency detection.

Chongyi Li
Nankai University
Biography:Chongyi Li, a professor and doctoral supervisor at Nankai University, is a recipient of the National Excellent Youth (Overseas) Fund. His primary research areas are computer vision and computational imaging. He has published over 80 academic papers in top international journals and conferences, such as TPAMI, TIP, NeurIPS, ICML, ICLR, CVPR, ICCV, and ECCV. Among these publications, 13 papers are highly cited according to the Essential Science Indicators (ESI), and 3 papers are considered ESI hot papers. One of his papers received a nomination for the Best Paper Award in Pattern Recognition. His technical achievements have been applied in core products of companies like Huawei and SenseTime. He has been recognized as one of the top 2% global scientists by Stanford University on two occasions. He has served or is currently serving as an editorial board member for SCI journals including IEEE TCSVT, IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, and Neurocomputing. Additionally, he has been a guest editor for IJCV. Furthermore, he has taken on important roles in the academic community, such as chairing or being a senior committee member for NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks, AAAI, and BMVC. He has also organized workshops for CVPR and ECCV. Furthermore, he is an IEEE Senior Member.
Speech Title:Underwater Image Enhancement — Opportunities and Challenges
Abstract:The application of underwater images in various fields is of great significance for advancing scientific research, protecting the marine environment, developing marine resources, and ensuring marine safety. These images provide valuable data and visual information, helping us to better understand and utilize marine resources, while also protecting the marine ecological balance and maintaining the health of ecosystems. However, the acquisition and processing of underwater images are relatively difficult, mainly due to issues such as light attenuation, light scattering, color loss, water flow interference, and the complexity of the underwater environment. In this report, I will briefly review the series of work conducted by our research group in the field of underwater image enhancement in recent years, explore the challenging issues currently faced in this research field, and conclude by providing a brief overview of the main research directions our research group plans to pursue in this area, along with some reflections on existing problems.
Machine Vision and Learning
Introduction
Machine learning is the art of exploring unknown laws and patterns from known data, and how to achieve better learning results with less cost has always been a core problem to be solved. With the development and application of machine learning technology in the field of vision, traditional learning algorithms are gradually pushing forward, while various deep learning methods are also evolving, in this workshop we will invite domain experts as speakers, share their latest work in this field, summarize the recent progress in the field of machine vision and learning and look forward to the future research directions. This workshop is supported by Technical Committee on Machine Vision.
Schedule
Sept. 22th 15:45-17:45
Organizers

Lin Zhouchen
Peking University
Biography:Zhouchen Lin, Professor of Peking University, IAPR/IEEE/CSIG Fellow. His research interests include machine learning and numerical optimization. He has published more than 230 papers and 2 books in English. He has won the first prize of the 2020 CCF Science and Technology Award. He has served as the (Senior) Area chair of CVPR, ICCV, NIPS/NuerIPS, ICML, IJCAI, AAAI and ICLR, former associate editor of IEEE T. Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, current associate editor of International J. Editorial Board Member of Computer Vision, Optimization Methods and Software.

Wang Yisen
Peking University
Biography:Yisen Wang is an assistant professor at Peking University. His research interests include machine learning theory and algorithms, focusing on adversarial robustness, graph learning, and weak/self-supervised learning theory. He has published more than 50 top papers in the field of machine learning, including ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, etc., and many of them have been selected as Oral or Spotlight. He has won the Best Paper Award of ECML 2021.
Presenters

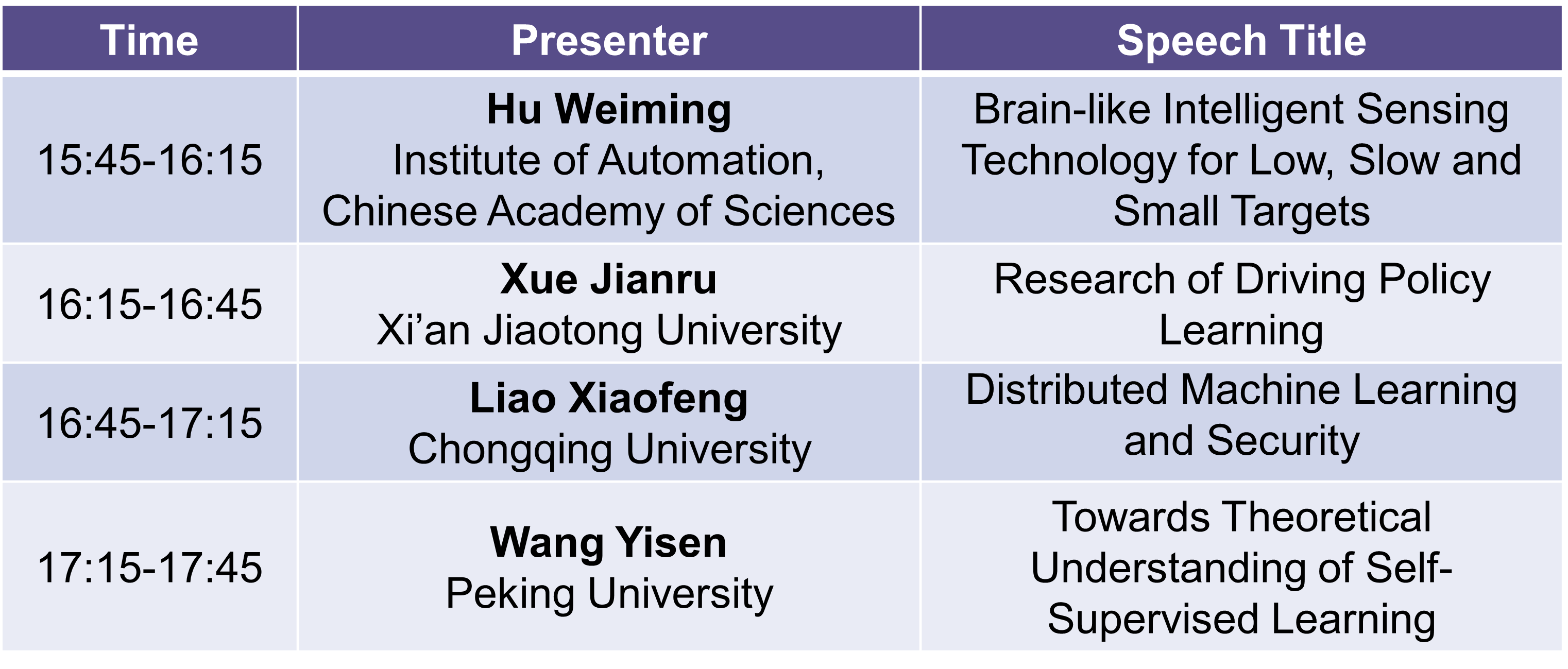
Hu Weiming
Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Biography:Weiming Hu, researcher at Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, leader of the video content security research team. His research direction is the sensitive content identification in network multimedia, etc. He has published more than 300 papers in international journals such as PAMI and IJCV, and international academic conferences such as ICCV, ECCV, CVPR, etc., and has been authorized more than 50 invention patents. The sensitive multimedia recognition and other technologies completed by the team have been practically applied to more than 100 enterprises and institutions, and have played a role in actual combat and achieved significant economic and social benefits. He won the second prize of National Natural Science Award, the first prize of Beijing Science and Technology (Technical Invention Category), the first prize of Beijing Invention Patent Award and the first prize of Wu Wenjun Artificial Intelligence Science and Technology Award.
Speech Title:Brain-like Intelligent Sensing Technology for Low, Slow and Small Targets
Abstract:In this talk, we analyze the relationship between neuroscience and computer vision. The enlightenment points of neuroscience for computer vision are summarized in several aspects: A) the characteristics of the basic visual cortex; B) the principle of the primary visual cortex extends to higher regions; C) Forward, reverse and lateral connections; D) cognitive mechanisms of visual nerve stratification; E) selective attention mechanisms of the visual nervous system; F) Selective memory mechanisms of dynamic information. This talk introduces our team’s research work in infrared image low-slow target tracking based on modal transfer and fusion perception, low-slow object tracking based on object size attention, online learning and target tracking based on recurrent least squares estimation inspired by brain-like continuous learning, detection-segmentation integration based on multi-task reciprocal dual-flow neural network, distillation learning based on neural center regulation and model compression and object classification with unified neuronal clipping mode, and single-stage online real-time multi-target tracking without anchor frames.

Xue Jianru
Xi’an Jiaotong University
Biography:Jianru Xue, professor of Xi’an Jiaotong University. His research interests include computer vision, pattern recognition, machine learning, and autonomous driving. He and his team won the IEEE ITSS Institute Lead Award in 2014, and the best application paper award in Asian Conference on Computer Vision 2012. He has published 100+ papers in top cited journals and conferences including IEEE TPAMI/TIP/TSMCB, CVPR, ICCV, ECCV, ICRA etc.
Speech Title:Research of Driving Policy Learning
Abstract:At present, applications of autonomous systems can be found in many fields. However, traditional pipeline of implementing sensing-action is found difficult to cope with open and dynamic environments, showing problems such as weak adaptability, poor self-learning ability and low efficiency. How to achieve human-like level autonomous behavior generation still faces great challenging problems. Based on the research experience of my research group for many years, I will talk about autonomous behavior generation of intelligent physical agent from the perspective of machine learning, in particular focusing on the two core topics, long-term situation prediction and policy learning, as well as latest progress we have made.

Liao Xiaofeng
Chongqing University
Biography:Xiaofeng Liao, professor, IEEE Fellow, AAIA Fellow. He has been engaged in the research of dynamic system theory, chaotic cryptography, cloud security and big data privacy protection of artificial neural networks. In the past 30 years, he has published more than 400 journal papers with more than 30,000 citations (Google Scholar). For 8 consecutive years, he has been selected as the highly cited scholars in computer science in China by Elsevier. He is the associate editor of international journals such as IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, and Electronic Journal.
Speech Title:Distributed Machine Learning and Security
Abstract:This talk explores the optimization and security issues of distributed machine learning. With the popularity of big data and machine learning applications, distributed machine learning has become one of the key technologies to solve large-scale data processing and modeling. However, distributed machine learning also faces many optimization and security challenges. In terms of optimization, distributed machine learning requires processing of large-scale data, as well as the complexity of synchronization and communication between different compute nodes. In order to solve these problems, the team proposes many optimization strategies and algorithm frameworks, such as gradient tracing, stochastic gradient, asynchronous execution, etc., which can effectively improve the efficiency and performance of distributed machine learning. On the security side, distributed machine learning faces threats such as data privacy leakage, model leakage, and malicious attacks. In order to protect the security of data and models, the team proposes many security technologies and mechanisms, such as cryptography, differential privacy, multi-party computing, etc., which can effectively protect the privacy and security of data and models. Overall, the optimization and security of distributed machine learning are two important issues in the field. Through continuous research and innovation, we can better solve these problems and provide better support and guarantee for the application of distributed machine learning.

Wang Yisen
Peking University
Biography:Yisen Wang is an assistant professor at Peking University. His research interests include machine learning theory and algorithms, focusing on adversarial robustness, graph learning, and weak/self-supervised learning theory. He has published more than 50 top academic papers in the field of machine learning, including ICML, NeurIPS, ICLR, etc., and many of them have been selected as Oral or Spotlight. He has won the ECML 2021 Best Paper Award.
Speech Title:Towards Theoretical Understanding of Self-Supervised Learning
Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) is an unsupervised approach for representation learning without relying on human-provided labels. It creates auxiliary tasks on unlabeled input data and learns representations by solving these tasks. SSL has demonstrated great success on various tasks. The existing SSL research mostly focuses on improving the empirical performance without a theoretical foundation. While the proposed SSL approaches are empirically effective on benchmarks, they are not well understood from a theoretical perspective. In this talk, I will introduce a series of our recent work on theoretical understanding of SSL, particularly on contrastive learning and masked autoencoders.
Youth Forum for Trustworthy Visual Computing
Introduction
Artificial intelligence technology is advancing at a fast pace, and trustworthy visual computing is emerging as a key research area in image and graphics. Trustworthy visual computing aims to use trustworthy computing techniques to ensure that image and video processing is private, secure, reliable and trustworthy. This research area has great implications for protecting personal privacy, preventing image and video data from being manipulated, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of image and video processing, and offering reliable visual information services for various domains such as smart city, smart healthcare, smart transportation, smart security and more. However, trustworthy visual computing also faces many challenges and issues, such as data quality, data security, data privacy, data ethics and more. This forum is designed to provide a platform for young scholars in trustworthy visual computing to share and learn from each other, to foster the research and development of trustworthy visual computing, and to promote the application and dissemination of related technologies. Moreover, this forum will also give participants a chance to present their research achievements, which will benefit their academic exchange and career development. This workshop is supported by CSIG Youth Working Committee.
Schedule
Sept. 22th 15:45-17:45
Organizers

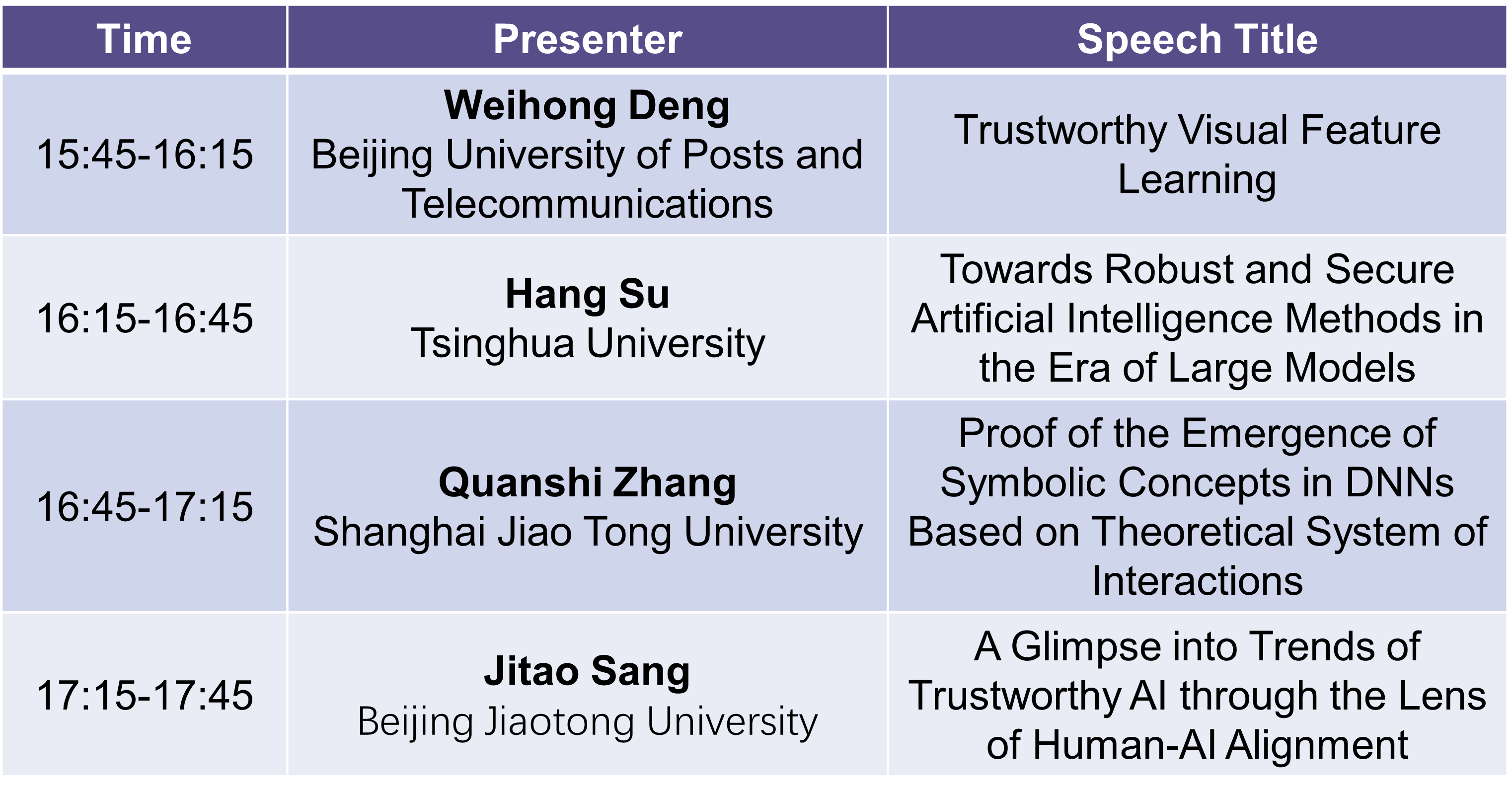
Peng Hu
Sichuan University
Biography:Peng Hu is currently an associate researcher at the College of Computer Science, Sichuan University. From 2019 to 2020, he was a research scientist at Institute for Infocomm, Research Agency for Science, Technology, and Research (A*STAR) Singapore. He received his Ph.D. degree in computer science and technology from Sichuan University, China, in 2019. His current interests mainly focus on multi-view learning, cross-modal retrieval, and network compression. On these areas, he has authored more than 20 articles in the top-tier conferences and journals.

Lei Zhu
Shandong Normal University
Biography:Zhu Lei is a professor at Shandong Normal University. His main research focus is on cross-modal analysis and retrieval. He has published over a hundred papers in CCF A-class conferences and ACM/IEEE journals. Additionally, he has authored two academic monographs and has eight highly cited papers in the ESI database, with over 6300 Google citations. Zhu Lei’s research has received Best Paper Nominations at ACM SIGIR 2019 and ACM MM 2019, as well as the Best Paper Award at CCF C-class conference ADMA 2020 and the Best Student Paper Award at ChinaMM 2022. One of his papers was selected as one of China’s top 100 most influential international academic papers in 2019. He also holds 22 authorized patents. Zhu Lei serves as an Associate Editor for international journals such as ACM TOMM, IEEE TBD, and Information Sciences. He is the Area Chair for ACM MM and a Senior Program Committee member for SIGIR, CIKM, and AAAI. He is also the Deputy Secretary-General of the Youth Working Committee of the China Society of Image and Graphics (CSIG). Zhu Lei has led or participated in over 10 cross-disciplinary research projects, including projects funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. He has received several awards, including the ACM China SIGMM Rising Star Award, the Outstanding Master’s Supervisor Award from the China Automation Society, the Returned Overseas Chinese Entrepreneurship Award from Shandong Province, and the Outstanding Service Award from CSIG’s Youth Working Committee.

Meina Kan
Institute of Computing Technology (ICT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS)
Biography:Meina Kan is an Associate Professor and Ph.D supervisor with the Institute of Computing Technology (ICT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). She received the Ph.D degree in computer vision from the Institute of Computing Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (ICT, CAS) in 2013. She has won the 1st Place of IEEE FG’15 “Point and Shoot Face Recognition Challenge (PaSC)”, 2nd Place of IEEE ICCV’15 “Apparent Age Estimation Track of ChaLearn Looking at People”, and 2nd Place of IEEE CVPR’17 “Landmark Detection Track of Faces in-the-wild Challenge”. Besides, her research is / was supported by National Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars and Beijing Nova Program.
Presenters

Deng Weihong
Beijing University Of Posts and Telecommunications
Biography:Weihong Deng is currently a Professor of the School of Artificial Intelligence, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Young Changjiang Scholar of the Ministry of Education, research direction is biometric identification, affective computing, multimodal learning. In recent years, he has presided over more than 20 national key research and development projects and projects of the National Natural Science Foundation of China. He has published more than 100 papers in international journals and conferences such as IEEE TPAMI, IJCV, TIP, ICCV, CVPR, and ECCV, and has been cited by Google Scholar for more than 13,000 times. He has served as the field chairman of CVPR, ECCV, ACMMM, IJCAI and other conferences for many times. He has been selected as Beijing Excellent Doctoral Dissertation, Beijing Science and Technology Rising Star, New Century Outstanding Talent of the Ministry of Education, and Elsevier China Highly Cited Scholar.
Speech Title:Trustworthy Visual Feature Learning
Abstract:Massive labeled data and deep learning technology have promoted the widespread application of visual recognition, and the performance of existing models on data sets has surpassed that of human eyes. However, in the real world, challenges such as data noise, environmental and regional differences, forgery and adversarial attacks lead to unsatisfactory stability of most visual recognition applications, and even cause ethical issues such as racial bias and security issues such as forged images. At the same time, privacy protection and data security have also aroused widespread concerns. Facing the above safe and credible identification problems, this report will report recent research progress in the following areas: 1) Stability feature learning under noisy labels; 2) Feature decoupling and confrontation robust feature learning for weak signals; 3) Fairness and adaptive feature learning under data bias. 4) Federated and incremental feature learning under privacy-preserving conditions.

Su Hang
Tsinghua University
Biography:Su Hang, Associate Researcher in the Department of Computer Science at Tsinghua University. His main research focuses on adversarial machine learning and robust visual computing and other related fields. He has published more than 100 papers in CCF recommended A-class conferences and journals, with over 6,000 citations on Google Scholar. He has received many academic awards, including the Wu Wenjun Artificial Intelligence Natural Science First Prize, ICME Platinum Best Paper, MICCAI Young Scholar Award, and AVSS Best Paper. He has led his team to win championships in various international academic competitions, such as the adversarial attack and defense at NeurIPS2017.
Speech Title:Towards Robust and Secure Artificial Intelligence Methods in the Era of Large Models
Abstract:With the rapid development of large models such as GPT, artificial intelligence systems are accelerating technological revolution and industrial progress, gradually integrating into human daily life. In this context, it is particularly important to ensure the safety and reliability of artificial intelligence systems. The current artificial intelligence generally lacks robustness, is easily deceived and misled, bringing security risks to its large-scale application and deployment. This report will focus on the challenges in the security of deep learning algorithms, starting from the basic principles of adversarial robustness, and introduce in detail the risk identification methods of deep learning models based on adversarial attacks. At the same time, the report will elaborate on the robust deep learning algorithms developed on this basis to enhance the safety and stability of the model. Finally, we will discuss the real risks of adversarial attacks in the physical world, providing inspiration for future research on safe artificial intelligence.

Quanshi Zhang
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Biography:Dr. Quanshi Zhang is an associate professor at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China. He received the Ph.D. degree from the University of Tokyo in 2014. From 2014 to 2018, he was a post-doctoral researcher at the University of California, Los Angeles. His research interests are mainly machine learning and computer vision. In particular, he has made influential research in explainable AI (XAI) and received the ACM China Rising Star Award. He was the co-chairs of the workshops towards XAI in ICML 2021, AAAI 2019, and CVPR 2019. We is the speaker of the tutorials on XAI at IJCAI 2020 and IJCAI 2021.
Speech Title:Proof of the Emergence of Symbolic Concepts in DNNs Based on Theoretical System of Interactions
Abstract:Although the interpretability of deep neural networks has received increasing attention in recent years, some fundamental problems have not been well formulated. For example, people still do not know (1) whether we can prove or disprove that a DNN inference can be explained as symbolic logic, and (2) what is the first principal that determines the robustness and generalization power of a DNN. Clarifying such fundamental problems will provide more alternative roads for the development of artificial intelligence. Therefore, in this talk, the speaker will mainly introduce new progresses in the theoretical system of interactions, which are developed by the research group of the speaker in recent two years, including the proof of the emergence of symbolic interactive concepts in DNNs, the proof of the mathematical connection between interactive concepts and a DNN’s generalization power and robustness, how to reformulate the various attribution-explanation methods into the unified paradigm of re-allocating interactions, etc.

Sang Jitao
Beijing Jiaotong University
Biography:Sang Jitao is a professor and the director of the Department of Computer Science at Beijing Jiaotong University. He is also a selected participant in the National Talent Youth Program. His main research interests include social media computing, multi-source data mining, and trustworthy machine learning. He has received awards such as the Special Award from the President of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the ACM China Rising Star Award. As the principal investigator, he has undertaken key projects funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the (first batch) Next Generation Artificial Intelligence Major Project, and the Beijing Outstanding Youth Foundation. He has received paper awards at international conferences recommended by the China Computer Federation (CCF) seven times as the first or second author. He has also received the first prize in Natural Science from the Chinese Institute of Electronics and the Beijing Science and Technology Award as the second contributor.
Speech Title:A Glimpse into Trends of Trustworthy AI through the Lens of Human-AI Alignment
Abstract:Human-AI alignment aims to ensure that AI systems meet human needs and conform to ethical values. The development of deep neural networks has initially achieved the alignment of AI capabilities. However, for large-scale applications in broader and deeper scenarios, further value alignment is needed. This is the goal of trustworthy AI, which includes reliability – interpretability, algorithmic fairness, and safety – adversarial robustness, and data privacy protection. With the rise of large models, machine learning models are transitioning from specialized tools to general-purpose intelligent agents. The study of value alignment and trustworthy AI is undergoing changes in research objects, alignment goals, and application scopes. However, the realization of value alignment might lead to an “alignment tax” problem, where AI capabilities may decline. How to maintain capability alignment while ensuring value alignment, or even achieving capability surpass, is an important issue in future trustworthy AI research.
Remote Sensing Image Processing
Introduction
In the past few decades, remote sensing image processing technology has been widely used in military, meteorology, agriculture, geology, environment and other fields. In recent years, with the continuous development of remote sensing technology and sensor technology, the spectral resolution, spatial resolution and temporal resolution of remote sensing images have been improved significantly, and the types of data available are also rich, covering visible light, infrared and radar, making traditional remote sensing image processing methods face new challenges. This workshop intends to invite four well-known experts in the field of remote sensing image processing as speakers to share their latest research progress in this field, and look forward to the future direction worth exploring. This workshop is supported by Technical Committee on Remote Sensing Image and Graphics.
Schedule
Sept. 22th 15:45-17:45
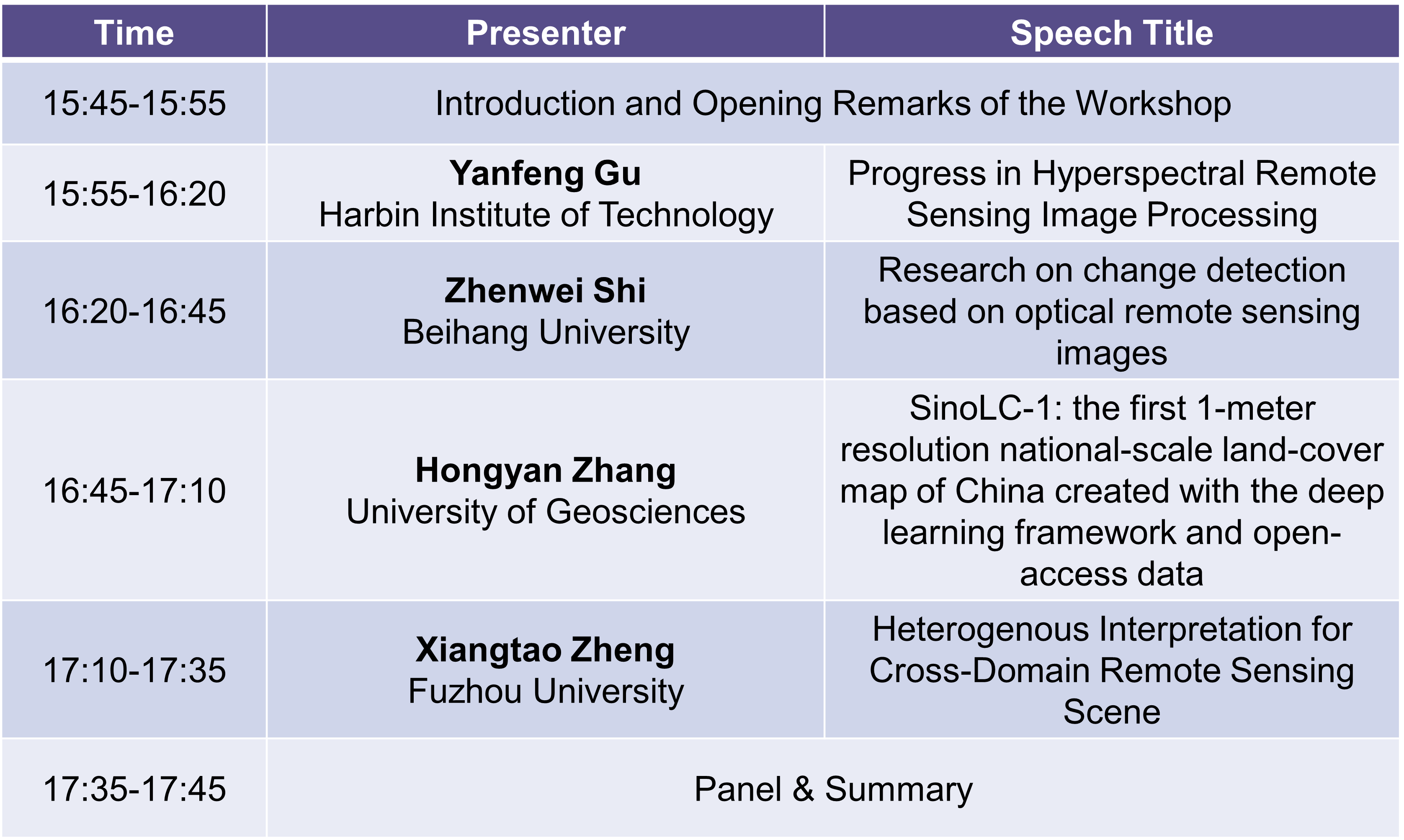
Organizers

Xian Sun
Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Biography:Xian Sun is a Professor and doctoral supervisor at the Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences. He has been engaged in key technology research of intelligent analysis of remote sensing data in China for a long time. He won 1 first prize of National Science and Technology Progress (Sequence 5) and 4 provincial and ministerial awards such as the Outstanding Achievement Award of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. He has published more than 70 SCI papers, 12 ESI highly cited papers, published 2 monographs, and authorized 24 invention patents. He was selected for the National Young Talent Program and the Young Scientist Award of the Chinese Command and Control Society. He is the co-chair of IEEE GRSS IADF-MIA, the secretary-general of Remote Sensing Image Committee of China Society of Image and Graphics, and the deputy editor/editorial board member of IEEE GRSL, PRL, TVCJ, ISPRS Journal, JSTARS, RS and other international remote sensing and artificial intelligence academic journals.

Renlong Hang
Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology
Biography:Renlong Hang is an associate professor at the School of Computer, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology. He is mainly engaged in pattern recognition, remote sensing image analysis, and intelligent interpretation of meteorological big data. He has published more than 40 papers in the international journals and conferences such as IEEE TGRS/TIP/TCSVT and AAAI, which have been cited more than 2800 times in total, and many papers have been selected as ESI highly cited papers. His research has been supported by many projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province. He has won the Jiangsu Province Excellent Doctoral Dissertation Award, PRCV 2018 Best Student Paper Award, and CCCV 2017 Best Student Paper Nominate Award. Now, he serves as a Topical Editor of IEEE-JSTARS journal.
Presenters

Yanfeng Gu
Harbin Institute of Technology
Biography:Hosting Project of the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, winner of national high-level talents, young and middle-aged scientific and technological innovation leader of the Ministry of Science and Technology, vice president of the School of Electronic and Information Engineering of Harbin Institute of Technology, second-class professor, doctoral supervisor, member of China Remote Sensing Application Association, director of Heilongjiang Key Laboratory of Sky Earth Integration Intelligent Remote Sensing Technology, IEEE Earth Science and Remote Sensing Journal Associate Editor, Young editorial board member of Science in China: Technical Science. Long term commitment to space intelligent information processing and space intelligent remote sensing research, and has won provincial and ministerial level scientific and technological awards multiple times.
Speech Title:Progress in Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image Processing
Abstract:Hyperspectral remote sensing detection has become one of the key technologies in the fields of high-resolution earth observation, deep space exploration, aerospace and national defense, with its outstanding advantages of high Spectral resolution and spectrum integration. As a branch of optical remote sensing, hyperspectral imaging is still affected by factors such as atmospheric conditions, environmental lighting, and spatial information degradation, resulting in difficulties in interpretation and application. The report will briefly introduce hyperspectral remote sensing image processing technologies around the removal of hyperspectral image uncertainty, multispectral to hyperspectral super-resolution reconstruction, and stereo hyperspectral interpretation.

Zhenwei Shi
Beihang University
Biography:Zhenwei Shi is a Professor of Beihang University, the Director of Aerospace Information Engineering Department (Image Processing Center), School of Astronautics, a winner of National Outstanding Youth Science Fund (2021). In the field of remote sensing image processing and computer vision, he has published more than 200 scientific research papers (including 100 IEEE journal papers and more than 100 SCI papers as the first or corresponding author). His research work has been funded by more than 50 projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation and the National Key R&D Program of China. To meet the major needs of aerospace defense and livelihood protection, the research results have been applied to a total of 20 types of military/civilian satellites. He is the editorial board member of seven domestic and foreign journals, including IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing and Pattern Recognition. He was a member of the board of the Chinese Association of Image and Graphics.
Speech Title:Research on change detection based on optical remote sensing images
Abstract:Mastering land use and land cover and analyzing land change are important contents of geographical monitoring. Efficient acquisition of accurate and objective land changes can provide decision-making support for relevant government departments. The popularization of multi-temporal high-resolution remote sensing images provides data guarantee for large-scale and fine land analysis. In recent years, the rise of artificial intelligence technologies such as image recognition based on deep learning has promoted changes in the field of remote sensing. Compared with traditional visual interpretation methods, remote sensing interpretation technology based on deep learning can automatically analyze the types of ground objects in images, showing great potential in terms of accuracy and efficiency. This report will focus on the topic of optical remote sensing image change detection. Starting from the background of remote sensing image change detection, it will introduce relevant traditional methods and give some change detection methods based on deep learning. The relevant technologies involved include network structure design (deep convolutional networks, Transformer), data augmentation methods (style transfer, image synthesis) and so on. The report also involves the preliminary exploration of the author’s team in the practical implementation of large-scale change monitoring of multi-temporal remote sensing images, and finally gives the prospect of the direction of change detection.

Hongyan Zhang
University of Geosciences
Biography:Prof. Hongyan Zhang received the Ph.D. degree in photogrammetry and remote sensing from Wuhan University in 2010, and was appointed as Full Professor there in 2016. He is currently the dean of Computer School, China University of Geosciences. His research interests mainly focus on image reconstruction for quality improvement, hyperspectral information processing and agricultural remote sensing. Dr. Zhang has authored/co-authored 98 journal citation report (JCR) papers, inlcuding 3 ESI Hot Papers and 16 ESI Highly Cited Papers. Prof. Zhang is a Senior Member of IEEE, and has been recognized as the 2021 and 2022 Chinese Highly Cited Scholar by Elsevier. Meanwhile, he has served as the Associate Editor for IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, Computers & Geoscience and Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing.
Speech Title:SinoLC-1: the first 1-meter resolution national-scale land-cover map of China created with the deep learning framework and open-access data
Abstract:In China, the demand for a more precise perception of the national land surface has become most urgent given the pace of development and urbanization. Constructing a high-resolution (HR) land-cover dataset for China with national coverage, however, is a non-trivial task and thus, an active area of research impeded by the challenges of various landforms, manual annotation, and computational complexity. To fill this gap, we established a weakly supervised-based deep learning framework for large-scale cross-resolution land-cover mapping, which utilized the 10-m resolution land-cover products and Open Street Maps to construct training labels for the 1-m resolution national-scale Google Earth imagery. The framework resolved the label noise problem stemming from a resolution mismatch between images and labels by combining a resolution-preserving backbone, a weakly supervised module, and an unsupervised loss function. Based on the structures, the framework enables to capture the reliable information from the 10-m resolution labels and complete the 1-m resolution national-scale land-cover mapping process. We took about 10 months to finish the first 1-m resolution national-scale land-cover map of the entire China (SinoLC-1) by processing over 73 TB of remote sensing data. The SinoLC-1 product was validated using a visually interpreted validation set including over 100,000 random samples and a statistical validation set from the 3rd national land resource survey report provided by the government. The validation results showed SinoLC-1 achieved an overall accuracy of 73.61% throughout the whole country.

Xiangtao Zheng
Fuzhou University
Biography:Xiangtao Zheng is currently a Professor with Fuzhou University. His main research interest is cross-domain scene interpretation. He has published 52 SCI papers, 14 papers were selected as ESI highly cited papers, and 13 national invention patents were authorized. He is an Associate Editor for IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Youth Editorial Board Member for CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, Editorial Board Member for Mathematics, Guest Editor for Remote Sensing and National Remote Sensing Bulletin.
Speech Title:Heterogenous Interpretation for Cross-Domain Remote Sensing Scene
Abstract:The remote sensing images are observed by multi-scale, multi-platform, and multi-view. This report focuses on the heterogenous interpretation technology for cross-domain remote sensing images. We aim to explore challenges faced by remote sensing images such as multi-scale, model solidification, and spatial-spectral representation. To tackle the issue of multi-scale in remote sensing images, we present a scale-independent multi-scale pooling representation and a scale-dependent cross-scale difference representation. Furthermore, a multi-task learning framework and a co-training framework are proposed to exploit the model’s dependence during training. Finally, a rotation-invariant network is proposed to extract rotation invariant spectral-spatial features from HSI patches.
